With an increasing number of confirmed covid-19 cases making news every hour, the fear and anxiety around it is also growing. Currently, proactive social distancing, containment through contact tracing, and significantly enhanced testing strategy followed by effective quarantine of positive cases are key steps to battle the pandemic.
In unlock 2.0, however, people have started moving out in higher numbers leading to a surge in the cases, which is expected to hit the peak in August. To make matters worse, recently the World Health Organization (WHO) admitted to the possibility of airborne transmission of covid-19 during certain medical procedures and in crowded indoor settings with poor ventilation.
Amidst all this, it is natural to wonder how you can prepare yourself for getting tested for covid-19, and what happens when you get tested. Here’s exactly what you need to know.
Who should get tested?
According to the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR), an individual experiencing influenza-like illness (ILI) should seek medical attention and get tested for covid-19. ILI case is defined with acute respiratory infection with fever more than or equal to 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit and cough; while a severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) case is defined as one with acute respiratory infection with fever more than or equal to 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit and cough and requiring hospitalisation.

After being exposed to the novel coronavirus, a person can start experiencing these symptoms anytime between 14 days of exposure. Despite the medical information about the disease still emerging, it is now, by and large, accepted that often people do not display signs of covid-19. These asymptomatic individuals should only be checked if they have been in contact of a confirmed case, and in case they were the first contacts they should be tested once between day five and day 14.
With the increasing number of cases, the ICMR has advised states and union territories to enable all qualified medical practitioners–government doctors and private practitioners–to prescribe a coronavirus test to any individual fulfilling the criteria for testing as per the ICMR guidelines.
What are the types of tests being used to counter covid-19?
There are two categories of covid-19 tests. The first category includes molecular testing (RT-PCR, TrueNat, CBNAAT) and antigen-based test—these tests can detect the virus in the body.
The second category—called serologic test—can detect antibodies produced in the human body to protect it against the virus. While the tests under the first category can determine if the person is infected currently, the serology test can only tell if the person has been infected in the past.
Large private labs are primarily using molecular testing techniques to conduct covid-19 tests, as it remains the gold standard for detecting viruses. However, in its revised guidelines, ICMR has now approved testing through rapid antigen tests.
Rapid antigen tests have been hailed by experts for speeding up the test-track-treat process. That said, anyone who tests negative for covid-19 by rapid antigen testing should certainly be sequentially tested by RT-PCR to rule out infection, whereas a positive result need not be confirmed by RT-PCR test and should be considered as a true positive result.
Select Topics of your interest and let us customize your feed.
PERSONALISE NOWThe other covid test approved by the ICMR is the antibody test. Antibodies are proteins produced by your immune system in response to an infection. After infection with the covid-19 virus, it can take two to three weeks to develop enough antibodies to be detected in an antibody test, so it’s important that you’re not tested too soon.
The antibody test is used for retrospective serosurveillance and helps in allaying the fear and anxiety of vulnerable populations like healthcare workers, frontline workers, immune-compromised individuals, individuals in containment zones etc.
What does this testing process entail?
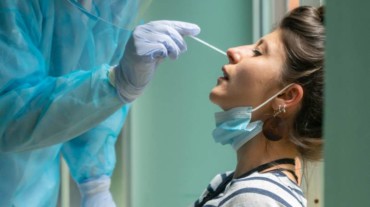
The RT-PCR technique can deliver reliable test results within six to eight hours on an average. For this technique, a sample is collected from deep inside your nose and the back of your throat with a swab (also known as the nasopharyngeal swab).

On the other hand, the antigen-based test is a rapid point-of-care test that directly detects the presence or absence of an antigen in the patient’s body, generating diagnosis results within 30 minutes. The test is performed to quickly detect fragments of proteins found on or within the virus by testing samples collected from the nasal cavity using swabs.
SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing involves taking a blood sample which is then examined for two types of antibodies—IgM/IgG antibodies. To conduct an antibody test for covid-19, typically a phlebotomist takes a blood sample, usually by a finger prick or by drawing blood from a vein in your arm. Then the sample is tested in a lab to determine whether you’ve developed antibodies against the covid-19 virus.
Until more is known, even if your test results show that you have covid-19 antibodies, continue to take precautions—including wearing a face mask in public, frequently washing your hands and practicing social distancing—to avoid the risk of spreading the virus.
Get Latest Updates on Preventive Care, Family Care, Reproductive Care, Self Care